ACL Surgery
USD ACL Surgery onwards
An anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction surgery can repair a torn or injured Anterior cruciate ligament (ACL)). The main function of ACL is to prevent the shinbone from moving forward.
The ACL is one of the four ligaments that keep the knee joint in a stable position. It connects the femur or the thigh bone with the tibia or the shin bone and runs diagonally across the middle of the knee joint.
An ACL injury is common among those who take part in sports and games. Abrupt stops, sudden turns, pivots, mistimed jumps, etc. can injure the ACL.
Other reasons include direct trauma to the knee, falls, sudden twisting of the knees, etc.
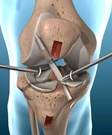
The most common injury to the ACL is a complete tear. A torn ACL will need ACL reconstruction surgery to repair it. During the operation, a tendon graft replaces the torn ligament.
ACL surgery is usually an arthroscopic or a ‘keyhole’ surgery. It reduces the chances of complications and offers a faster recovery.
Causes of ACL injury
It is one of the most common sports injuries, which accounts for more than 80% of all sports injuries. The sports that create maximum damage to ACL are football, rugby, basketball, cricket, tennis, and volleyball.
The main reasons for ACL injury are:
- Sudden slowing down and change of direction. E.g., Football, Rugby, Cricket
- Pivoting on a firm foot. E.g., Basketball
- Landing from a jump incorrectly or landing on a single leg. E.g., Volleyball, Basketball, Long jump
- Stopping abruptly while running. E.g., Tennis
- Direct blow to the knee or the outside of the leg. E.g., Football, Volleyball, Rugby, Basketball.
Though commonly regarded as a sports injury, an ACL tear can also occur because of damage to the knees, a sudden change in posture, and falls.
Interestingly, females are more prone to ACL injury than males. Persons in the age group of 15 to 45 years are more affected, maybe due to their more active lifestyle.
Symptoms of an ACL tear or injury
An ACL injury is usually of sudden onset, and the symptoms also appear at the same time. The most common signs that you will have are:
- A popping sound in the knee at the time of injury
- Sudden swelling of the knees
- Sharp pain in the knees
- Weakness and instability of the knees
If the tear is complete, you will find it difficult to walk or even stand up. You should not walk without support then, or else there can be more complications.
Risk factors for ACL injury
Certain factors increase one’s chances of having an ACL injury. They include
- Being a woman - Women are more prone to tear than men. Reason can be the difference in anatomy, muscle strength and influence of hormones
- Sudden movements during sports or games- Sudden and jerky movements during sports activities can damage the ligament.
- A lack of warm-up before sports or games- Improper or no warm-up can increase the risk
- Use of ill-fitting shoes or sandals
- Reduced muscle strength- This puts lots of pressure in the ligaments
- Playing on surfaces not meant for a particular sports
ACL surgery procedure
Before surgery
Before the surgery, you will undergo a routine medical check-up to assess your health status. Medications like blood thinners and certain herbal supplements will have to be stopped before surgery to avoid bleeding.
If you are a smoker, you should avoid this during the recovery period. Or else, it may interfere with wound healing and delay your recovery.
You will be in the hospital for two or three days and will be able to carry out routine activities only after a week. So, proper arrangements should be made at home and in the workplace during this period. You will be admitted to the hospital a day before the surgery.
During surgery
The ACL reconstruction surgery is done either under general or epidural anesthesia. With general anesthesia, you will sleep through the procedure. In epidural anesthesia, you will be awake during the procedure, but will not feel any pain.
An arthroscopic ACL surgery is preferable to open surgery for many reasons. A smaller incision wound, fewer complications, and a faster recovery are some of them.
The duration of the surgery will be around two hours.
During the surgery, the surgeon will remove your torn ACL and replace it with a graft. This graft usually is from tendons around the knee. Patellar tendon grafts and hamstring tendon grafts are the most commonly used ones.
The surgeon makes two or three small incisions on the sides of your knees to insert an arthroscope. The arthroscope has a camera to view the knee joint from inside. The other incisions will carry surgical drills, suction tubes, and other instruments needed for surgery.
The surgeon then drills small holes on the ends of the tibia and femur bones to make small tunnels. These tunnels serve as anchors to the graft. The surgeon then fixes the graft tissue into these tunnels and fastens them using screw or staples. After this, the surgeon closes the incision.
After surgery
Once the surgery is over, you will be in the recovery room for some time. When you wake up from your sleep, You will find that there is a tight bandage around your knee.
Once the effects of anesthesia wear off, you will go back to your room. You might have a little pain, and painkillers will take care of it. Icepacks will be applied over your knee to reduce the swelling.
You will use crutches to move around in the room. You should be careful to avoid pressure on the affected knee. Moving around will improve your blood circulation and will aid in faster recovery. It will also help to prevent blood clots from forming n the deep veins of your legs.
Recovery from ACL surgery
While you will be able to walk properly without crutches after ten days of ACL surgery, complete recovery may take around six months. A well-structured ACL rehab protocol is essential for a quick recovery. Doctors would suggest an appropriate rehabilitation program for you, which will then be administered by qualified physiotherapists.
Your recovery program would typically be along the following path
1. Weeks 1 & 2
The main focus is to reduce the swelling in the joints and to increase the range of motion. You will be on crutches generally for 7-10 days after the surgery. You may take pain killers in case the pain is persistent.
The physical therapy regime should start extensively during this period with a focus on knee movements – bending, straightening, and raising the affected leg.
2. Weeks 2 - 6
By now, swelling and inflammation would have settled. The key objective now would be to strengthen the leg muscles, especially quadriceps. You can start more intense exercises and activities like swimming and cycling during this period.
If you have an office/desk job, you could start working from week 3 or 4 onwards. You could also resume driving the car in 3-4 weeks after the surgery.
3. Weeks 6-24
You will be able to return to regular activity during this period except for sports, which require sudden turning, twisting, stopping, or turning.
If you are doing a manual job, you will be able to return to work by around the 12thweek.
You will be able to return to active sports in about six months.
Risks and complications of ACL surgery
With modern surgical techniques and the high skill level of doctors, the success rate of ACL surgery is around 90%. However, as with any other surgery, ACL surgery also carries some amount of risk with it. The most common risks include
- Infection – Even though the chances of infection from the surgical wounds are less than 1%, antibiotics would be given after the surgery to prevent it.
- Blood clot – Again, the chances are very less (less than 0.1%). However, the doctors may give medication if there is any risk found during the evaluation.
- Knee pain- This is common after ACL surgery, with about 2 people out of 10 affected by pain, especially around the knee cap after the surgery. However, a proper rehabilitation regime can help you to recover from the pain.
- Stiffness- This is also a common complaint that requires an extensive physical therapy rehabilitation program.