Understanding the Signs and Symptoms of Brain Cancer
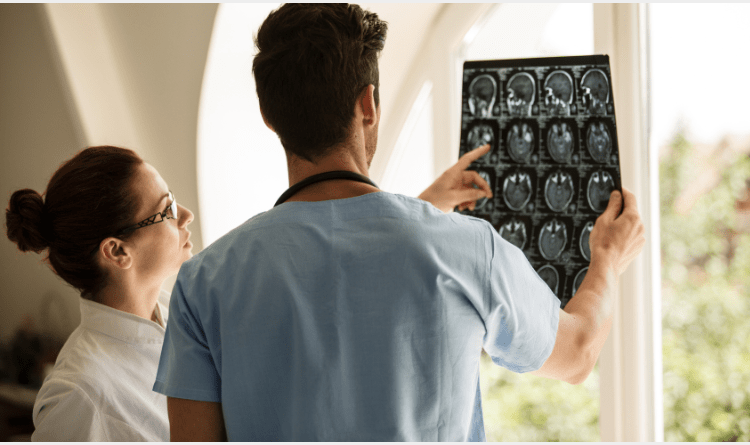
Understanding the Signs and Symptoms of Brain Cancer
Brain cancer results from cancerous cell growth in the brain that forms masses called brain tumors. According to Global Cancer Statistics 2020, 308,102 new brain and central nervous system cancer cases were diagnosed, and 251,329 cancer-related deaths occurred in 2020 worldwide.
The cancer cells from tumors can be slow or fast-growing, depending on the type. More than 40 major types of brain tumors that exist are grouped into two main classes:
Primary Cancer - It begins in the brain and may spread to other parts of the nervous system. Usually, it does not spread outside the brain and spinal cord.
Secondary Cancer or Metastasis - It starts in another part of the body and spreads to the brain. Common cancers that may spread to the brain include:
Breast cancer
Colon cancer
Kidney cancer
Lung cancer
Skin cancer (melanoma)
Types of Brain Cancer
All brain cancers are tumors, but not all brain tumors are cancerous.
Non-cancerous Brain Tumors (Benign Brain Tumors):
- Typically grow slowly
- Have distinct borders
- Rarely spread
- It can damage and compress parts of the brain, causing severe dysfunction
- Benign tumors can become malignant very rarely
- Examples: meningioma, vestibular schwannoma, and pituitary adenoma
Cancerous Brain Tumors (Malignant Brain Tumors):
- Grows rapidly
- Invade surrounding healthy brain structures
- Examples: olfactory neuroblastoma, chondrosarcoma, and medulloblastoma
According to the American Cancer Society (ACS), people have less than a 1% chance of developing a malignant brain tumor in their lifetime.
Types of Brain Tumor
The National Brain Tumor Society estimates that more than 120 types of brain tumors exist.
Some brain tumors, such as glioblastoma multiforme, are malignant and may be fast-growing. Other types, such as meningiomas and schwannomas, may be slow-growing and benign.
Some most common types of brain tumors are:
Glioma - The most common type of primary brain tumor, gliomas, originate in the glial (supportive) cells and account for about 3/10 cases of brain cancer.
Astrocytoma is a type of glioma that includes glioblastomas, a fast-growing type of brain tumor.
Meningioma tumors are often benign and slow-growing. They grow in the tissue surrounding the brain and spinal cord. These are the most common types of brain tumors in adults.
Gangliogliomas are slow-growing tumors found in the neurons and glial cells that can usually be treated with surgery.
Craniopharyngiomas are slow-growing tumors between the pituitary gland and the brain and often press on optic nerves, resulting in vision difficulties.
Schwannomas are slow-growing tumors around the cranial nerves and are almost always benign.
Medulloblastoma is a fast-growing tumor on the brain's nerve cells and is more common in children.
What Causes Brain Cancer?
There is no definitive cause of brain cancer, and the risk factors are much less defined than in other cancers.
Some genetic conditions and environmental factors that may contribute to the development of the disease include:
Compromised immune system
Exposure to certain industrial chemicals or solvents
Previous radiation treatment
Genetic links
Are Brain Tumors Hereditary?
Less than 5% of brain tumors are a result of genetics. Some inherited conditions that put individuals at greater risk of developing tumors include:
Neurofibromatosis
Von Hippel-Lindau disease
Li-Fraumeni syndrome
Familial adenomatous polyposis
Lynch syndrome
Basal cell nevus syndrome (Gorlin syndrome)
Tuberous sclerosis
Cowden syndrome
Who Gets Brain Cancer?
Most cases are diagnosed in people 65 or older, and the risk increases. Women are twice as likely to develop meningiomas, while medulloblastomas, predominantly diagnosed in children, are more frequently found in men.
Men are at a slightly higher risk, about 1 in 140, while women have a one in 190 chance of getting brain cancer. Certain types of brain tumors are more likely to occur in women.
Inconclusive cancer research indicates that chemical exposure may lead to a higher incidence of brain tumors in people working in oil refining, rubber manufacturing, and drug manufacturing.
Signs and Symptoms of Brain Cancer
The general symptoms of brain cancer may include the following:
A headache that changes depending on the time of day and position of the head and worsens over time
Seizures
Numbness
Nausea or vomiting
Memory loss
Muscle weakness
Speech difficulty
The symptoms also depend on the affected parts of the brain, which include:
Frontal Lobe -
Difficulty with planning or organizing activities
Changes in behavior, personality, and social skills
Depression or mood swings
Weakness in part of the face or on one side of the body
Difficulty walking
Loss of sense of smell
Problems with seeing or speaking
Trouble finding the right word
Temporal Lobe -
Forgetting events and conversations
Difficulty understanding what is said to you
Trouble learning and remembering new information
Seizures with strange feelings, smells, or deja vu
Brain Stem -
Coordination problems
Difficulty swallowing or speaking
Double vision
Weakness and numbness in part of the face
Leg and arm weakness
Fatigue
Changes to sleep/wake patterns
Spinal Cord -
Back and neck pain
Numbness or tingling in arms or legs
Change to muscle tone in the arms or legs
Clumsiness or difficulty walking
Loss of bowel or bladder control (incontinence)
Even non-cancerous tumors often damage normal cells in the surrounding brain tissue, nerves, and blood vessels. This damage can cause side effects, such as headaches, fatigue, double vision, or blurred vision.
How to Diagnose Brain Cancer?
Healthcare professionals use the following tools to diagnose brain cancer:
Biopsy
Laboratory tests, including advanced genomic testing
Nuclear medicine bone scan
Angiography
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
Computed tomography (CT) scan
Positron emission tomography (PET) scan
Treatment of Brain Cancer
Healthcare providers use a combination of therapies to treat cancer. Treatment options include the following:
Surgery: Brain surgery (neurosurgery or craniotomy) is the most common treatment for brain tumors. Surgery may also include: Intraoperative neuronavigation (a brain-mapping procedure), Intraoperative electrophysiology brain-mapping (motor mapping and language mapping), and Intraoperative radiation therapy (IORT).
Chemotherapy includes local chemotherapy and systemic chemotherapy.
Radiation therapy uses X-rays, external beam radiation, and whole-brain radiation.
Combination therapy: Receiving both chemotherapy and radiation therapy is called combination therapy.
Biologic drugs boost, direct, or restore your body's natural defenses against your tumor. For example, immunotherapy increases the ability of the immune system to target and fight cancer.
Other medications: The doctor may prescribe medications to treat symptoms and side effects.
Clinical trials: Clinical trials for brain cancer could include immunotherapy and CAR T cell therapy trials.
Rehabilitation: Provided if cancer or its treatment affects the ability to talk, walk, or perform other daily functions. It includes physical, occupational, and other therapies to help patients relearn these activities.
Alternative therapies: Some healthcare professionals recommend a balanced diet and vitamin and mineral supplementation to replace nutrients lost from cancer treatment. Consult your doctor before taking supplements or herbs, changing your diet, or pursuing alternative therapies.
Cost of Brain Cancer Treatment
The cost of brain cancer treatment varies depending on the following few factors:
Age of the patient
Severity or metastasize of the tumor
The medical condition of the patient
Type of surgery
Post-procedure complications that are involved
Any other lab tests or examination tests such as X-ray, ECG, etc.
Patients look for quality treatment along with a budget-friendly cost. Because of the complexity and variation in cancer treatment, it is difficult to predict the total costs for any individual at the time of diagnosis.
If talking about quality, it is worth noting that brain surgery success rates in Germany are among the highest in the world. Also, relapse after treatment rarely occurs. Treatment of brain tumors in Germany is so successful due to the high qualification of specialists and the availability of high-precision equipment. The cost of treatment in Germany is lower than that in the USA.
Cost Comparison of Brain Cancer Treatment
Treatment
Germany
USA
Chemotherapy
USD 1800 to USD 2200
USD 10,000 to USD 200,000
PET Scan
USD 1800 to USD 2200
USD 2200 to USD 10,700
Craniotomy Surgery
USD 9000 to USD 11000
USD 50,000 to USD 150,000
The treatment price in Germany depends on the prescribed course of therapy, which is selected individually.
Know more about the cost of Brain Cancer treatment in India, UK and the USA.
Conclusion
Not all brain tumors are cancerous, and about two-thirds are benign. Your healthcare team will develop an individualized and thorough treatment plan to help treat cancer and improve your quality of life. Brain cancer is frightening, but new treatments and research improve the odds and survival rates.
Get in Touch with Medical Experts
Most Searched Blog
Heart Surgery
Heart Transplant

Atrial Septal Defect